URBAN-ACT RESOURCES

PARTNERS

PUBLICATIONS AND REPORTS
Flagship Reports
Policy Briefs
EFC Assessments
Working Papers
WEBINARS (2025)
 Nature-Based Solutions for Hot Cities
Nature-Based Solutions for Hot Cities
 Financing Energy Transition to Power Urban Futures
Financing Energy Transition to Power Urban Futures
 Rethinking Urban Waste: Circular Approaches to Minimize Methane Emissions
Rethinking Urban Waste: Circular Approaches to Minimize Methane Emissions
- Concept Note
- Slides
- Webinar Flyer
- Webinar Recording
 Pathways to Low Carbon People-Centred Urban Transport Systems
Pathways to Low Carbon People-Centred Urban Transport Systems
 Informal Settlements Driving the Transition to Climate-Resilient Cities
Informal Settlements Driving the Transition to Climate-Resilient Cities
 Innovative Land Use Tools for Building Climate-Ready Cities
Innovative Land Use Tools for Building Climate-Ready Cities
 Urban Solutions for Transboundary Air Pollution and Climate Change
Urban Solutions for Transboundary Air Pollution and Climate Change
 Mobilizing Innovative Climate Finance for Cities through Carbon Market Mechanisms
Mobilizing Innovative Climate Finance for Cities through Carbon Market Mechanisms
ENABLING CITY CLIMATE FINANCE
Accessing climate finance for urban development can be complex. However, cities can improve their chances of securing financing by following two key steps:
Step 1: Assessing Enabling Framework Conditions
Before cities can effectively access and deploy climate finance, it is essential to understand the national and subnational conditions that either support or hinder investment. These are known as enabling framework conditions (EFCs). EFCs are essential for scaling urban climate finance as they provide regulatory clarity, strengthen institutional capacity, mitigate investment risks, and promote stakeholder engagement, creating a conducive environment for national and subnational entities to drive climate action and achieve global climate goals.
EFCs can also be understood as the foundational conditions that enable the design, planning, and execution of effective climate action interventions, and are therefore integral across most of the climate action project value chain.
To support this process, Urban-Act and the Cities Climate Finance Leadership Alliance (CCFLA) have developed two complementary toolkits to assess both national and subnational EFCs, intended to enable better access to urban climate finance. The National and Subnational EFC Assessment Tool Workbooks, designed for use by national and subnational officials, use a standardized approach to evaluate four dimensions of EFCs: climate policy, budget and finance, climate data, and vertical and horizontal coordination. When used together, the tools can help assess EFCs, facilitate recommendations, and identify areas for improvement.


Already, EFC assessments have been successfully conducted in Indonesia, India, and Fiji. Please refer to the completed assessments below for inspiration and cross-learning from their experiences.
Accessing India’s Enabling Framework Conditions for Subnational Climate Finance
 Scaling finance for cities’ climate action requires sufficient enabling conditions at the national level. Enabling framework conditions (EFCs) can create a conducive environment for climate finance, thereby helping national and subnational entities to drive climate action and contribute to the achievement of climate goals. Such EFCs improve access to finance by creating the right policy environment, enabling cities’ access to finance, strengthening subnational climate data, and ensuring coordination from the national to the city level. This report presents findings from our pilot application in India of the CCFLA/Urban-Act National Assessment Tool, which evaluates countries’ national-level EFCs to mobilize subnational climate finance. DOWNLOAD
Scaling finance for cities’ climate action requires sufficient enabling conditions at the national level. Enabling framework conditions (EFCs) can create a conducive environment for climate finance, thereby helping national and subnational entities to drive climate action and contribute to the achievement of climate goals. Such EFCs improve access to finance by creating the right policy environment, enabling cities’ access to finance, strengthening subnational climate data, and ensuring coordination from the national to the city level. This report presents findings from our pilot application in India of the CCFLA/Urban-Act National Assessment Tool, which evaluates countries’ national-level EFCs to mobilize subnational climate finance. DOWNLOAD
 This report presents the findings from the EFC assessment of Coimbatore. ESCAP developed a subnational EFC assessment tool under the Urban Act Project. This tool evaluates city EFCs against subnational climate finance. As part of the DA16 global project, ESCAP intends to assess and strengthen EFCs and cities’ capacities to engage in climate action.
This report presents the findings from the EFC assessment of Coimbatore. ESCAP developed a subnational EFC assessment tool under the Urban Act Project. This tool evaluates city EFCs against subnational climate finance. As part of the DA16 global project, ESCAP intends to assess and strengthen EFCs and cities’ capacities to engage in climate action.
COMING SOON
 COMING SOON
COMING SOON
 COMING SOON
COMING SOON
 COMING SOON
COMING SOON
 COMING SOON
COMING SOON
 COMING SOON
COMING SOON
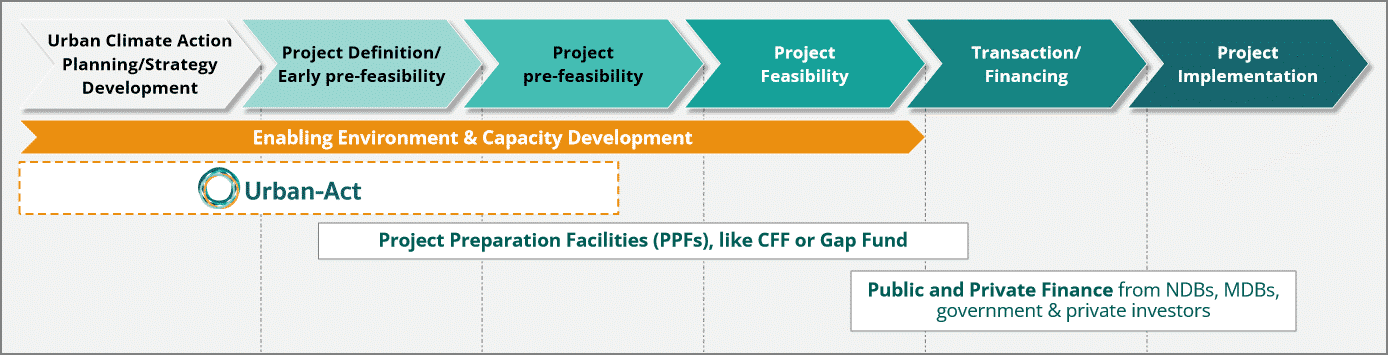
Step 2: Project Preparation and Financing through Matchmaking
Once national and subnational enabling environments are understood, cities then need to turn climate action ideas and project proposals into market-ready projects. This is where matchmaking comes in.
Matchmaking in this context refers to helping cities prepare bankable climate action projects ready for implementation finance by connecting them with project preparation facilities (PPFs). PPFs support cities in developing project concepts, conducting (pre-)feasibility studies, and accessing later-stage financing—whether from domestic budgets or international financial institutions. This process ensures that projects meet investor criteria while remaining aligned with national policy frameworks, overcoming existing barriers and enabling climate finance at the city level.
In the climate action project value chain, project preparation and matchmaking act as the bridge between early project definition and securing implementation finance, ensuring that promising ideas are translated into structured, bankable interventions.
Please see the below matchmaking protocol for accelerating access to climate finance for your city.